Which Group Has The Highest Ionization Energy
pythondeals
Nov 29, 2025 · 7 min read
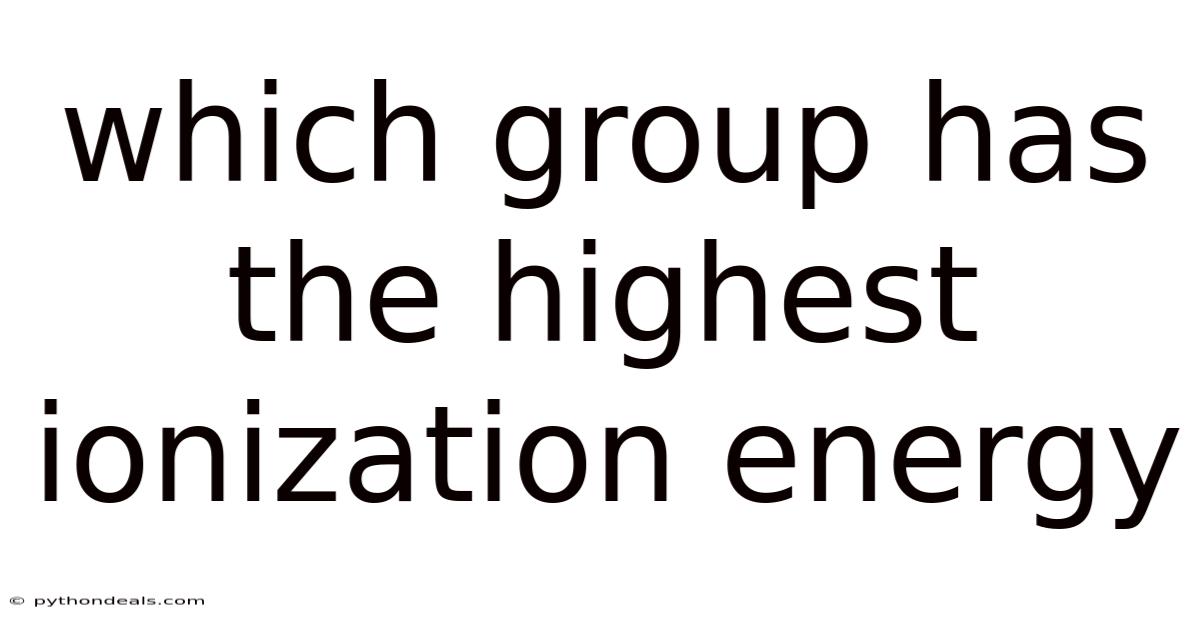
Table of Contents
Let's dive into the fascinating world of chemistry to uncover which group on the periodic table boasts the highest ionization energy. Understanding ionization energy is crucial for grasping how elements interact and form chemical bonds. It's a fundamental concept that governs many chemical properties and reactions.
Ionization energy, in its simplest definition, is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. This energy is a measure of how tightly an atom holds onto its electrons. The higher the ionization energy, the more difficult it is to remove an electron, indicating a strong attraction between the electron and the nucleus. Several factors influence ionization energy, including nuclear charge, atomic radius, and electron shielding. Let’s delve deeper into these factors before identifying the group with the highest ionization energy.
Factors Influencing Ionization Energy
- Nuclear Charge: The greater the positive charge in the nucleus (i.e., more protons), the stronger the attraction for electrons, leading to higher ionization energy.
- Atomic Radius: As the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons increases (larger atomic radius), the attraction weakens, decreasing ionization energy.
- Electron Shielding: Inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the full attractive force of the nucleus. Greater shielding reduces the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outer electrons, thus lowering ionization energy.
- Electron Configuration: The electron configuration of an atom significantly affects ionization energy. Atoms with full or half-full electron shells tend to have higher ionization energies because these configurations are particularly stable.
Now that we have a basic understanding, let's move on to explore which group exhibits the highest ionization energy.
Comprehensive Overview
The periodic table is organized into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows), with elements in the same group sharing similar chemical properties. Ionization energy generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group from top to bottom. This trend is due to the interplay of the factors mentioned above.
- Across a Period: As we move across a period, the nuclear charge increases while the atomic radius generally decreases. The increasing nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus, and the decreasing atomic radius means the outer electrons are already closer to the nucleus. These factors combine to increase the ionization energy.
- Down a Group: As we move down a group, the atomic radius increases significantly, and the number of inner electrons increases, resulting in greater shielding. The outer electrons are further from the nucleus and shielded from its full positive charge, making them easier to remove and reducing the ionization energy.
So, considering these trends, which group has the highest ionization energy? It's the noble gases (Group 18).
The Noble Gases (Group 18): A Detailed Look
The noble gases, also known as inert gases or rare gases, include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). These elements are characterized by their exceptional stability and lack of reactivity. This stability arises from their electron configurations, specifically their full valence electron shells. Helium has a full 1s shell with two electrons (1s²), while the other noble gases have full ns²np⁶ valence shells with eight electrons.
Here's why noble gases have the highest ionization energies:
- Full Valence Shells: A full valence shell represents an extremely stable electron configuration. Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of a noble gas. However, noble gases already possess this stable configuration, making them highly resistant to losing an electron.
- High Effective Nuclear Charge: Noble gases experience a high effective nuclear charge. While they have inner electrons that provide some shielding, the outermost electrons still experience a significant pull from the nucleus. This strong attraction makes it difficult to remove an electron, hence the high ionization energy.
- Compact Atomic Size: Noble gases, particularly those in the earlier periods, have relatively small atomic radii. The smaller the atom, the closer the electrons are to the nucleus, and the stronger the attraction. This is especially true for helium, which has the highest ionization energy of all elements.
To illustrate the magnitude of ionization energies for noble gases, consider these values (in kJ/mol):
- Helium (He): 2372
- Neon (Ne): 2081
- Argon (Ar): 1521
- Krypton (Kr): 1351
- Xenon (Xe): 1170
- Radon (Rn): 1037
As you can see, these values are significantly higher than those of elements in other groups. For comparison, the first ionization energy of sodium (Na), an alkali metal in Group 1, is only 496 kJ/mol.
Historical Context
The discovery of noble gases in the late 19th century revolutionized chemistry. Initially, they were considered "inert" because they did not readily form compounds. This lack of reactivity was attributed to their stable electron configurations and high ionization energies. However, in the 1960s, chemists began to synthesize compounds containing noble gases, demonstrating that they were not entirely inert under extreme conditions. This breakthrough expanded our understanding of chemical bonding and reactivity.
Trends & Recent Developments
While noble gases are generally unreactive due to their high ionization energies, recent research has focused on creating novel compounds and exploring their potential applications. For instance, xenon compounds, such as xenon hexafluoride (XeF₆), have been synthesized and studied extensively. These compounds are used in various applications, including as fluorinating agents and in materials science.
Moreover, researchers are investigating the use of noble gas elements in plasma technologies, lighting, and medical imaging. For example, xenon is used as an anesthetic and in MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to enhance image contrast. The unique properties of noble gases, including their high ionization energies and distinct emission spectra, make them valuable in these technological applications.
Tips & Expert Advice
- Understand the Periodic Trends: Grasping the periodic trends in ionization energy is crucial for predicting the chemical behavior of elements. Remember that ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Focus on Electron Configuration: Pay close attention to the electron configurations of elements, especially the valence electron configurations. Full or half-full electron shells lead to greater stability and higher ionization energies.
- Consider Effective Nuclear Charge: Evaluate the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outer electrons. A higher effective nuclear charge means a stronger attraction and higher ionization energy.
- Compare Ionization Energies: When comparing the ionization energies of different elements, consider the successive ionization energies. The energy required to remove the first electron is generally lower than the energy required to remove the second electron, and so on.
- Explore Noble Gas Compounds: Investigate the chemistry of noble gas compounds to understand how these elements can be forced to form chemical bonds under specific conditions. Research the synthesis, properties, and applications of compounds like xenon fluorides.
FAQ
Q: Why is ionization energy important?
A: Ionization energy is a fundamental property that helps us understand the chemical reactivity of elements. It determines how easily an atom can lose electrons and form positive ions (cations), which is crucial for understanding chemical bonding and the formation of compounds.
Q: How does ionization energy relate to electronegativity?
A: Both ionization energy and electronegativity are related to the electron-attracting ability of an atom. Ionization energy measures the energy required to remove an electron, while electronegativity measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have high electronegativities.
Q: Does ionization energy change for successive electron removals?
A: Yes, ionization energy increases for successive electron removals. The first ionization energy (IE₁) is the energy required to remove the first electron, the second ionization energy (IE₂) is the energy required to remove the second electron, and so on. IE₂ is always greater than IE₁, because it is more difficult to remove an electron from a positively charged ion than from a neutral atom.
Q: What is the difference between ionization energy and electron affinity?
A: Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, whereas electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to an atom. Ionization energy is always positive (endothermic), while electron affinity can be either positive or negative (exothermic).
Conclusion
In summary, the noble gases (Group 18) possess the highest ionization energies due to their stable, full valence electron shells, high effective nuclear charge, and compact atomic size. Understanding ionization energy is essential for predicting the chemical behavior of elements and their ability to form chemical bonds. The unique properties of noble gases make them valuable in various technological applications, and ongoing research continues to explore their potential in new and exciting ways.
How do you think the discovery of noble gases has impacted modern chemistry, and what future applications of these elements are you most excited to see?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Si Unit For Work Is
Nov 29, 2025
-
Fertilization Typically Takes Place In The
Nov 29, 2025
-
A Foodborne Illness Is Defined As
Nov 29, 2025
-
Gravitational Pull Between Earth And Moon
Nov 29, 2025
-
How To Get Concentration From Absorbance
Nov 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Group Has The Highest Ionization Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.