What Are The First 15 Perfect Square Numbers
pythondeals
Dec 06, 2025 · 10 min read
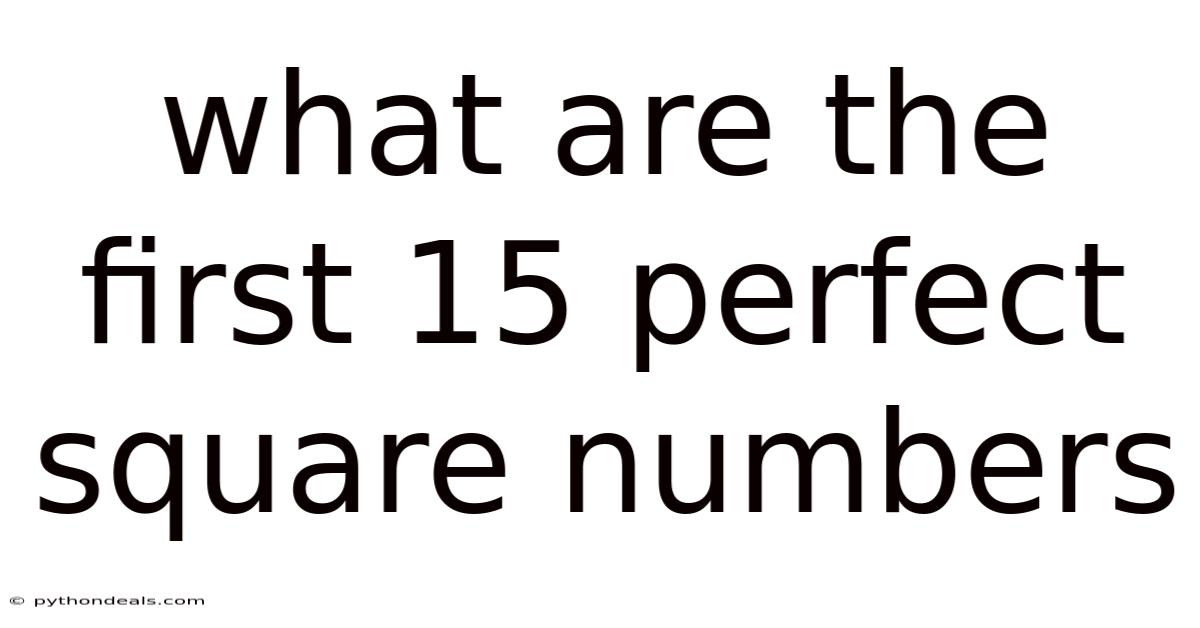
Table of Contents
Perfect squares are fundamental concepts in mathematics, representing the result of squaring an integer. Understanding these numbers provides a foundation for various mathematical operations and problem-solving. In this article, we will delve into the first 15 perfect square numbers, exploring their properties, significance, and practical applications.
Introduction
Perfect squares are integers that can be obtained by squaring another integer. In simpler terms, a perfect square is the product of an integer multiplied by itself. These numbers hold a special place in mathematics due to their unique properties and applications in algebra, geometry, and number theory. Understanding the first few perfect squares is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematical reasoning.
What is a Perfect Square?
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. For example, 9 is a perfect square because it is the result of (3 \times 3), which is (3^2). Similarly, 16 is a perfect square because it is the result of (4 \times 4), or (4^2). Perfect squares are always non-negative since squaring any real number (positive, negative, or zero) will result in a non-negative value.
The First 15 Perfect Square Numbers
Now, let's identify the first 15 perfect square numbers. These are obtained by squaring the first 15 positive integers:
- 1: (1^2 = 1 \times 1 = 1)
- 4: (2^2 = 2 \times 2 = 4)
- 9: (3^2 = 3 \times 3 = 9)
- 16: (4^2 = 4 \times 4 = 16)
- 25: (5^2 = 5 \times 5 = 25)
- 36: (6^2 = 6 \times 6 = 36)
- 49: (7^2 = 7 \times 7 = 49)
- 64: (8^2 = 8 \times 8 = 64)
- 81: (9^2 = 9 \times 9 = 81)
- 100: (10^2 = 10 \times 10 = 100)
- 121: (11^2 = 11 \times 11 = 121)
- 144: (12^2 = 12 \times 12 = 144)
- 169: (13^2 = 13 \times 13 = 169)
- 196: (14^2 = 14 \times 14 = 196)
- 225: (15^2 = 15 \times 15 = 225)
These are the first 15 perfect square numbers. Understanding them is essential for recognizing patterns and applying them in more complex mathematical problems.
Comprehensive Overview
Perfect squares are more than just numbers; they are fundamental building blocks in various mathematical fields. Let's dive deeper into their properties and significance.
Properties of Perfect Squares
-
Non-Negativity: As mentioned earlier, perfect squares are always non-negative. This is because any real number squared results in a non-negative value.
-
Prime Factorization: The prime factorization of a perfect square contains only even exponents. For example, the prime factorization of 36 (which is (6^2)) is (2^2 \times 3^2). All exponents are even.
-
Units Digit Pattern: Perfect squares exhibit a unique pattern in their units digits. The possible units digits for a perfect square are 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, and 9. This pattern arises from the units digits of the numbers being squared:
- If the number ends in 0, its square ends in 0.
- If the number ends in 1 or 9, its square ends in 1.
- If the number ends in 2 or 8, its square ends in 4.
- If the number ends in 3 or 7, its square ends in 9.
- If the number ends in 4 or 6, its square ends in 6.
- If the number ends in 5, its square ends in 5.
-
Sum of Odd Numbers: Each perfect square can be expressed as the sum of consecutive odd numbers starting from 1. For instance:
- (1 = 1)
- (4 = 1 + 3)
- (9 = 1 + 3 + 5)
- (16 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7)
- (25 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9)
This property is useful in various mathematical proofs and problem-solving techniques.
-
Difference of Squares: The difference between consecutive perfect squares increases linearly. For example:
- (4 - 1 = 3)
- (9 - 4 = 5)
- (16 - 9 = 7)
- (25 - 16 = 9)
This property can be generalized as ((n+1)^2 - n^2 = 2n + 1), where (n) is an integer.
Significance and Applications
-
Algebra: Perfect squares are essential in algebra, particularly in factoring quadratic equations and simplifying expressions. Recognizing perfect square trinomials, such as (a^2 + 2ab + b^2) or (a^2 - 2ab + b^2), allows for efficient factorization.
-
Geometry: Perfect squares play a crucial role in geometry. For instance, the area of a square is a perfect square. The Pythagorean theorem, (a^2 + b^2 = c^2), involves perfect squares and is fundamental in determining the lengths of sides in a right-angled triangle.
-
Number Theory: In number theory, perfect squares are used in various theorems and proofs. They are also relevant in determining whether a number is a quadratic residue modulo another number.
-
Computer Science: Perfect squares are used in algorithms and data structures, particularly in scenarios involving optimization and indexing. For example, the square root of a number is often used in algorithms to improve efficiency.
-
Cryptography: Perfect squares are sometimes used in cryptographic algorithms to create secure keys and encrypt data. Their unique mathematical properties make them useful in generating complex and unpredictable sequences.
Examples and Illustrations
To further illustrate the significance of perfect squares, let's consider a few examples:
-
Factoring Quadratic Equations:
Consider the quadratic equation (x^2 + 6x + 9 = 0). Recognizing that (x^2 + 6x + 9) is a perfect square trinomial, we can factor it as ((x + 3)^2 = 0). Thus, the solution to the equation is (x = -3).
-
Pythagorean Theorem:
In a right-angled triangle with sides (a = 3) and (b = 4), the hypotenuse (c) can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
(c^2 = a^2 + b^2 = 3^2 + 4^2 = 9 + 16 = 25)
Since 25 is a perfect square ((5^2)), we can determine that (c = 5).
-
Sum of Consecutive Odd Numbers:
To find the perfect square equal to the sum of the first 7 odd numbers, we calculate:
(1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + 13 = 49)
Since 49 is a perfect square ((7^2)), this illustrates the property that the sum of the first (n) odd numbers is (n^2).
Tren & Perkembangan Terbaru
While the basic concept of perfect squares remains constant, their application in modern contexts continues to evolve. Here are some trends and recent developments:
-
Computational Mathematics: With the advent of powerful computers, perfect squares are used in complex algorithms for solving numerical problems, optimizing functions, and simulating physical phenomena. Advanced numerical methods often rely on properties of perfect squares to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
-
Data Analysis and Machine Learning: In data analysis, perfect squares can be used to normalize data, identify patterns, and build predictive models. Machine learning algorithms sometimes use squared terms to create non-linear models that can capture complex relationships in data.
-
Quantum Computing: In the emerging field of quantum computing, perfect squares and other mathematical concepts are used to develop quantum algorithms and protocols. Quantum computers leverage the unique properties of quantum mechanics to perform computations that are impossible for classical computers.
-
Cryptography and Cybersecurity: Cryptographic algorithms continue to evolve, with new methods being developed to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Perfect squares and related mathematical structures are used in the design of encryption schemes, digital signatures, and authentication protocols.
-
Educational Tools and Resources: There is a growing emphasis on interactive and engaging educational tools that help students understand mathematical concepts like perfect squares. Online platforms, educational games, and virtual simulations are used to make learning more accessible and enjoyable.
Tips & Expert Advice
Understanding and working with perfect squares can be made easier with a few strategic tips and expert advice:
-
Memorization: Memorizing the first few perfect squares can significantly improve your speed and accuracy when solving mathematical problems. Start with the first 15 perfect squares and gradually expand your knowledge.
-
Pattern Recognition: Practice recognizing patterns in perfect squares, such as the units digit pattern and the sum of odd numbers. This will help you quickly identify perfect squares in various contexts.
-
Prime Factorization: Use prime factorization to determine whether a number is a perfect square. If all exponents in the prime factorization are even, the number is a perfect square.
-
Estimation: Develop your ability to estimate square roots. This is particularly useful when working with large numbers. For example, you can estimate the square root of 200 by recognizing that it is between 14 ((\sqrt{196})) and 15 ((\sqrt{225})).
-
Practice Problem Solving: Solve a variety of problems involving perfect squares to reinforce your understanding. Focus on applying perfect squares in different contexts, such as algebra, geometry, and number theory.
-
Utilize Technology: Use calculators and software to assist with complex calculations and to verify your results. There are also many online resources and tools that can help you explore and visualize perfect squares.
-
Teach Others: Teaching others about perfect squares can deepen your own understanding. Explaining the concepts to someone else forces you to think critically and identify any gaps in your knowledge.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What is the square root of a perfect square?
A: The square root of a perfect square is an integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals the perfect square. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because (5 \times 5 = 25).
Q: Are perfect squares always positive?
A: Perfect squares are always non-negative. The square of any real number (positive, negative, or zero) will result in a non-negative value.
Q: Can a perfect square be a decimal or fraction?
A: A perfect square is an integer. However, the term "perfect square" can sometimes be loosely applied to decimals or fractions if they are the result of squaring a decimal or fraction. For example, 0.25 is the square of 0.5, and (\frac{1}{4}) is the square of (\frac{1}{2}).
Q: How can I quickly determine if a large number is a perfect square?
A: To quickly determine if a large number is a perfect square, you can use the units digit test. The number must end in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9. Additionally, you can estimate the square root and check if it is an integer. Prime factorization can also be used to verify if all exponents are even.
Q: What is the difference between a perfect square and a square root?
A: A perfect square is the result of squaring an integer, while the square root is the integer that, when squared, gives the perfect square. They are inverse operations of each other.
Conclusion
Perfect square numbers are a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching applications. The first 15 perfect squares—1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196, and 225—provide a solid foundation for understanding algebraic principles, geometric theorems, and various problem-solving techniques. By exploring their properties, patterns, and applications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for their significance in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding perfect squares is not just about memorizing numbers; it's about recognizing patterns, applying logical reasoning, and developing a keen sense of mathematical intuition. Whether you're factoring quadratic equations, calculating the area of a square, or exploring advanced concepts in number theory, perfect squares will undoubtedly play a crucial role in your mathematical journey.
How do you plan to incorporate your knowledge of perfect squares into your problem-solving approach? What other mathematical concepts are you interested in exploring to enhance your understanding of the world around you?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Living Things Contain Which Element
Dec 06, 2025
-
How Is Glucose Produced In Plants
Dec 06, 2025
-
A Brief History Of Ancient Greece
Dec 06, 2025
-
What Is Alert And Oriented X4
Dec 06, 2025
-
What Percentage Of Water Is The Body Made Of
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The First 15 Perfect Square Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.