Integration Of Ln X 2 1
pythondeals
Nov 30, 2025 · 7 min read
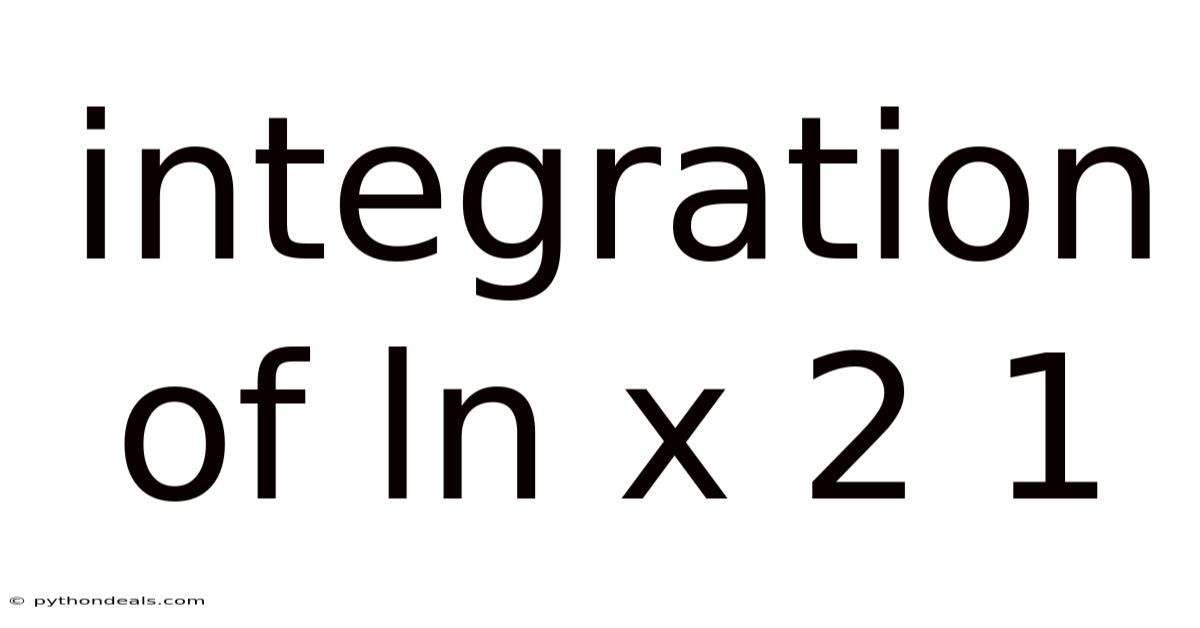
Table of Contents
Alright, let's dive into the fascinating world of integrating ln(x² + 1). This function pops up quite a bit in various mathematical and engineering contexts, and knowing how to handle its integral is a valuable skill. We'll break down the integration process step by step, explore the theory behind it, and provide some practical tips to make the journey smoother.
Introduction
Integrating functions involving logarithms can sometimes seem daunting, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable. The function ln(x² + 1) is particularly interesting because it combines a logarithmic function with a quadratic term, necessitating a careful strategy. Mastering this integration not only enhances your calculus skills but also provides a foundational understanding applicable in more complex scenarios.
Think of ln(x² + 1) as a function that appears frequently in applications involving distances, signal processing, and even probability distributions. Whether you’re a student tackling calculus problems or a professional needing to solve intricate models, understanding how to integrate this function is undeniably useful. This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of the process, ensuring you grasp both the method and the underlying rationale.
Comprehensive Overview
Definition and Background
The integral of ln(x² + 1) represents the area under the curve of this function. This area is defined by the antiderivative F(x) of ln(x² + 1), such that F'(x) = ln(x² + 1). Formally, we write:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = F(x) + C
where C is the constant of integration.
The function ln(x² + 1) itself is an even function, meaning f(x) = f(-x). This symmetry can sometimes be useful when dealing with definite integrals over symmetric intervals. However, for indefinite integration, we primarily focus on finding the antiderivative.
The Integration Challenge
Integrating ln(x² + 1) isn't straightforward because there's no direct integration rule that applies. We need to employ a more sophisticated technique: integration by parts. This method is particularly useful when dealing with products of functions, and by cleverly rewriting our integral, we can apply it effectively.
The integration by parts formula is:
∫ u dv = uv - ∫ v du
where u and dv are parts of the integrand chosen strategically to simplify the integral.
Why Integration by Parts Works
The integration by parts technique is derived from the product rule for differentiation. Recall that the product rule states:
(uv)' = u'v + uv'
Integrating both sides with respect to x, we get:
∫ (uv)' dx = ∫ u'v dx + ∫ uv' dx
Which simplifies to:
uv = ∫ v du + ∫ u dv
Rearranging this, we arrive at the integration by parts formula:
∫ u dv = uv - ∫ v du
The goal is to choose u and dv such that the new integral ∫ v du is simpler than the original integral ∫ u dv.
Step-by-Step Integration of ln(x² + 1)
Step 1: Choose u and dv
To apply integration by parts to ∫ ln(x² + 1) dx, we can choose:
- u = ln(x² + 1)
- dv = dx
This choice allows us to differentiate u and integrate dv, potentially simplifying the integral.
Step 2: Find du and v
Next, we need to find du and v:
-
Differentiating u = ln(x² + 1), we get:
du = (2x / (x² + 1)) dx
-
Integrating dv = dx, we get:
v = x
Step 3: Apply the Integration by Parts Formula
Now, we substitute u, v, du, and dv into the integration by parts formula:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = x ln(x² + 1) - ∫ x (2x / (x² + 1)) dx
This simplifies to:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = x ln(x² + 1) - 2 ∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx
Step 4: Simplify the New Integral
The new integral ∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx requires further manipulation. We can rewrite the integrand by adding and subtracting 1 in the numerator:
∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx = ∫ ((x² + 1 - 1) / (x² + 1)) dx
This allows us to separate the integral into two parts:
∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx = ∫ (1 - (1 / (x² + 1))) dx
Which simplifies to:
∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx = ∫ dx - ∫ (1 / (x² + 1)) dx
Step 5: Evaluate the Simplified Integrals
The two integrals we now have are standard integrals:
- ∫ dx = x
- ∫ (1 / (x² + 1)) dx = arctan(x)
So, we have:
∫ (x² / (x² + 1)) dx = x - arctan(x)
Step 6: Substitute Back into the Original Equation
Now, we substitute this result back into the integration by parts equation:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = x ln(x² + 1) - 2 [x - arctan(x)] + C
Which simplifies to:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = x ln(x² + 1) - 2x + 2 arctan(x) + C
Thus, the integral of ln(x² + 1) is:
∫ ln(x² + 1) dx = x ln(x² + 1) - 2x + 2 arctan(x) + C
Tren & Perkembangan Terbaru
While the integration technique itself is well-established, the application and relevance of integrals involving logarithmic and quadratic functions continue to evolve. Here are some current trends and developments:
-
Computational Tools: Modern computational software like Mathematica, Maple, and Python's SymPy library can easily handle such integrals. However, understanding the underlying methodology is crucial for interpreting and validating the results.
-
Machine Learning: In machine learning, logarithmic loss functions (like log loss) are frequently used in classification problems. Understanding how to analyze and optimize these functions often requires manipulating integrals similar to the one discussed here.
-
Signal Processing: Logarithmic functions appear in signal processing for dynamic range compression and analysis. Integration of these functions is essential in areas like audio processing and telecommunications.
-
Financial Modeling: In quantitative finance, stochastic calculus involves integrating complex functions, often including logarithmic terms. Models for asset pricing and risk management may benefit from techniques similar to those described here.
Tips & Expert Advice
-
Practice Regularly: Integration techniques, especially integration by parts, require practice. Work through a variety of examples to solidify your understanding.
-
Understand the Theory: Don't just memorize the steps. Understand why integration by parts works and how it is derived from the product rule of differentiation.
-
Check Your Work: After finding the integral, differentiate your result to ensure it matches the original function. This helps catch errors.
-
Use Computational Tools Wisely: While software can solve integrals, use these tools to verify your manual calculations rather than relying on them exclusively.
-
Recognize Patterns: As you solve more integrals, you'll start to recognize patterns that make it easier to choose u and dv effectively.
-
Simplify First: Before applying integration by parts, simplify the integrand as much as possible. This can reduce the complexity of the resulting integrals.
-
Consider Alternative Methods: Sometimes, other integration techniques (like trigonometric substitution or partial fractions) may be more efficient. Be flexible and consider different approaches.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Why do we use integration by parts for ln(x² + 1)?
A: Integration by parts is used because there is no direct rule for integrating ln(x² + 1). By choosing u = ln(x² + 1) and dv = dx, we can simplify the integral into a more manageable form.
Q: Can I use a table of integrals instead of integration by parts?
A: While a table of integrals might contain a similar form, it's essential to understand the derivation and application of the technique. Relying solely on tables can limit your problem-solving abilities.
Q: What is the significance of the constant of integration, C?
A: The constant of integration, C, represents the family of antiderivatives that differ only by a constant. When evaluating definite integrals, C cancels out, but it's crucial for indefinite integrals.
Q: How can I verify my solution to an integration problem?
A: Differentiate your result. If the derivative matches the original integrand, your integration is correct.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using integration by parts?
A: Common mistakes include incorrect choices of u and dv, errors in differentiation or integration, and forgetting the constant of integration.
Q: Can I use integration by parts multiple times in the same problem?
A: Yes, in some cases, you may need to apply integration by parts more than once to fully solve the integral.
Conclusion
Integrating ln(x² + 1) might have seemed intimidating at first, but by breaking it down step by step, we’ve shown that it's entirely manageable. The key takeaways include the strategic application of integration by parts, simplifying complex integrands, and understanding the underlying theory. Mastering these techniques not only equips you to handle similar problems but also deepens your understanding of calculus as a whole.
Now that you’ve walked through this detailed guide, how do you feel about tackling integrals of this nature? Are you ready to apply these techniques to new problems and solidify your skills? Remember, practice makes perfect, and the more you engage with these concepts, the more confident and proficient you’ll become. What other integration challenges would you like to explore next?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Optimal Temperature Range For Sperm Production Is
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Can You Tell If A Graph Is Linear
Nov 30, 2025
-
Is Formula Mass The Same As Molar Mass
Nov 30, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Argon Gas
Nov 30, 2025
-
Is Hcl A Base Or Acid
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integration Of Ln X 2 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.