All Sides Of Quadrilateral Are Equal
pythondeals
Dec 05, 2025 · 8 min read
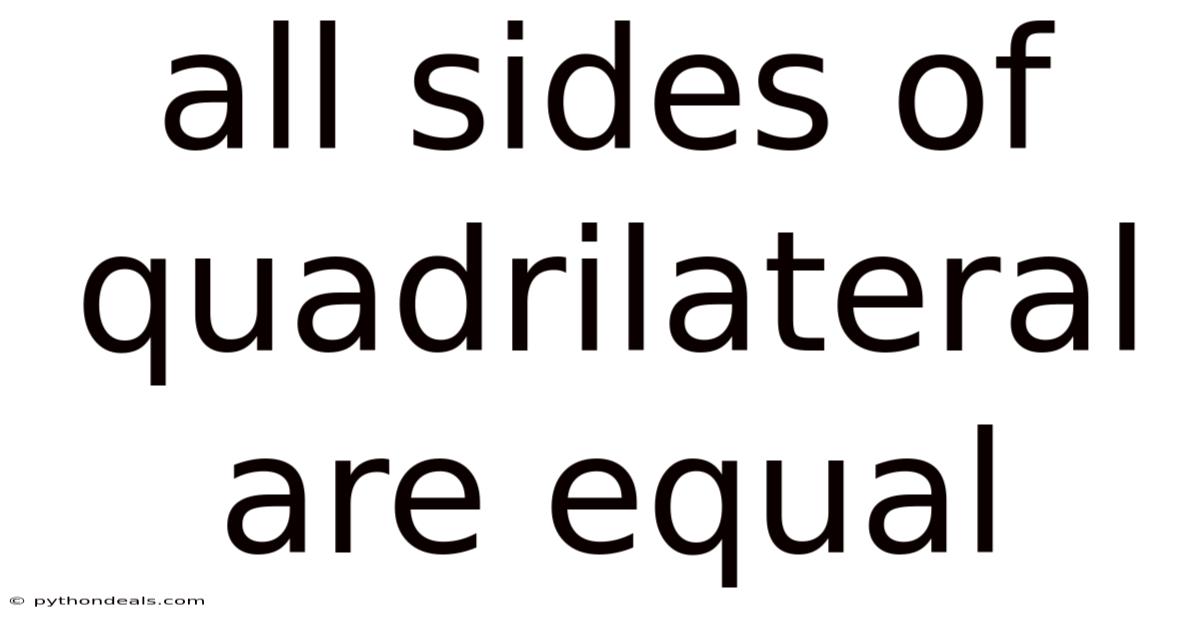
Table of Contents
Let's explore the fascinating world of quadrilaterals, focusing specifically on those special figures where all four sides are equal. This characteristic, seemingly simple, leads to a wealth of interesting properties and distinctions that separate these shapes from the broader family of four-sided polygons. We'll delve into the different types of quadrilaterals with equal sides, their unique characteristics, and the relationships they share with other geometric figures.
Quadrilaterals with Equal Sides: An Introduction
A quadrilateral, by definition, is a closed, two-dimensional shape with four sides and four angles. When all four sides of a quadrilateral are of equal length, we enter a more specific territory. While the equal side lengths impose a constraint, it doesn't automatically define a single, unique shape. Instead, it opens the door to a few key contenders: the rhombus and the square. Understanding the difference between these shapes lies in examining their angles.
The Rhombus: Equilateral with a Twist
The rhombus is defined as a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. This is its defining characteristic. However, unlike a square, the angles of a rhombus are not necessarily right angles. This freedom in angle measurement allows for a 'squashed' or tilted appearance, distinguishing it from its more rigid cousin.
Key Properties of a Rhombus:
- Equal Sides: All four sides are congruent.
- Opposite Angles Equal: Angles opposite each other are equal in measure.
- Opposite Sides Parallel: Opposite sides are parallel to each other. This automatically makes a rhombus a parallelogram.
- Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at their midpoints.
- Diagonals Perpendicular: The diagonals intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). This is a crucial property that distinguishes it from a general parallelogram.
- Diagonals Bisect the Angles: Each diagonal bisects the angles at the vertices it connects. This means the diagonal cuts the angle into two equal angles.
Calculating the Area of a Rhombus:
There are multiple ways to calculate the area of a rhombus, depending on the information available:
- Using Base and Height: Area = base * height. The 'base' is the length of one side, and the 'height' is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side.
- Using Diagonals: Area = (1/2) * d1 * d2, where d1 and d2 are the lengths of the two diagonals. This formula is particularly useful since you don't need to calculate the height.
- Using Trigonometry: If you know the side length ('s') and one of the angles (θ), you can use: Area = s² * sin(θ).
The Square: The Perfect Combination
The square is a special type of quadrilateral that combines the properties of both a rhombus and a rectangle. It's defined as a quadrilateral with all four sides equal and all four angles equal to 90 degrees (right angles). This combination of equilateral sides and equiangular corners creates a highly symmetrical and predictable shape.
Key Properties of a Square:
- Equal Sides: All four sides are congruent.
- Right Angles: All four angles are 90 degrees.
- Opposite Sides Parallel: Opposite sides are parallel.
- Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals intersect at their midpoints.
- Diagonals Perpendicular: The diagonals intersect at a right angle (90 degrees).
- Diagonals Bisect the Angles: Each diagonal bisects the angles at the vertices it connects (each angle becomes 45 degrees).
- Diagonals are Equal: Both diagonals have the same length.
Calculating the Area of a Square:
Calculating the area of a square is straightforward:
- Using Side Length: Area = side * side = s², where 's' is the length of one side.
Why are these Properties Important? A Deeper Dive
The properties listed above aren't just abstract geometric facts. They have real-world implications and are crucial for various applications:
- Engineering and Architecture: Squares and rhombuses are fundamental building blocks. Their predictable angles and side lengths are essential for creating stable and aesthetically pleasing structures. Think of the grid patterns in city planning, the bracing in bridges using rhombic structures for strength, and the precision cuts needed to create perfectly square tiles.
- Design: The symmetry and balance inherent in squares and rhombuses make them visually appealing. They are frequently used in graphic design, textiles, and patterns of all kinds. The 'golden ratio' often incorporates squares and rectangles in its construction, showcasing the inherent beauty in these simple shapes.
- Mathematics: These shapes serve as excellent examples for teaching geometric principles. They illustrate concepts like symmetry, congruence, parallelism, and angle relationships. Understanding the relationship between different quadrilaterals helps students grasp more complex geometric theorems.
- Computer Graphics: Squares and rhombuses are easily represented and manipulated in computer graphics. They are fundamental shapes used in creating 2D and 3D models.
Comprehensive Overview: Connecting the Dots
To truly understand quadrilaterals with equal sides, it's crucial to see how they relate to other geometric figures. Let's place them within the broader family of quadrilaterals and highlight their unique place.
-
Quadrilateral Hierarchy: The quadrilateral family is vast. At the top is the general quadrilateral, a simple four-sided figure. Within that, we have:
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. Crucially, a rhombus is a special type of parallelogram.
- Rectangle: A parallelogram with four right angles.
- Rhombus: A parallelogram with four equal sides.
- Square: A parallelogram with four equal sides and four right angles. It's both a rhombus and a rectangle.
-
The Interplay of Properties: Notice that the square inherits properties from both the rhombus and the rectangle. It has the equal sides of a rhombus and the right angles of a rectangle. This "inheritance" is a key concept in geometry.
-
Why are these shapes important in mathematics? The study of these quadrilaterals strengthens logical reasoning skills. Proofs related to their properties require careful deduction and application of geometric axioms. Understanding the relationships between these shapes fosters a deeper understanding of mathematical structure and logic.
Tren & Perkembangan Terbaru: Quadrilaterals in the Digital Age
While the properties of these shapes have been known for centuries, their application continues to evolve in the digital age.
- Algorithmic Art: Generative art algorithms often use geometric shapes, including squares and rhombuses, to create complex and visually stunning patterns. The predictable nature of these shapes makes them ideal for algorithmic manipulation.
- Data Visualization: Squares and rhombuses are used in data visualization techniques. For example, a 'treemap' uses nested rectangles to represent hierarchical data. The area of each rectangle corresponds to the value of the data it represents.
- Game Development: Squares and rhombuses are fundamental shapes in game development. They are used to create environments, characters, and objects. Their simple geometry makes them computationally efficient to render.
- Material Science: Rhombic structures are found in certain materials at the molecular level, influencing their properties like strength and flexibility. Researchers are exploring how to manipulate these structures to create new materials with desired characteristics.
Tips & Expert Advice: Working with Quadrilaterals
Here are some practical tips for working with quadrilaterals with equal sides:
-
Visualize the Properties: Don't just memorize the properties; visualize them. Draw different rhombuses and squares. Observe how changing the angles of a rhombus affects its shape and its diagonals. This hands-on approach will solidify your understanding.
-
Break Down Complex Problems: If you're faced with a complex problem involving a quadrilateral, try breaking it down into simpler components. Can you divide it into triangles? Can you use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of a diagonal? Strategic decomposition can often lead to a solution.
-
Use Coordinate Geometry: Placing a quadrilateral on a coordinate plane can be a powerful tool. You can use coordinate geometry to calculate distances, slopes, and angles. This approach is particularly useful for proving geometric theorems.
-
Master the Definitions: A strong grasp of the definitions is crucial. Be able to clearly define a rhombus, a square, a parallelogram, and a rectangle. Understand the subtle differences between them. This clarity will prevent confusion.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice: The best way to master quadrilaterals is through practice. Work through a variety of problems, from simple area calculations to more complex geometric proofs. The more you practice, the more comfortable you'll become with these shapes.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
Q: Is every square a rhombus?
- A: Yes, because a square has four equal sides, which is the defining characteristic of a rhombus.
-
Q: Is every rhombus a square?
- A: No, because a rhombus doesn't necessarily have four right angles, which is required for a square.
-
Q: Can a quadrilateral with equal sides be a trapezoid?
- A: No, a trapezoid only requires at least one pair of parallel sides. A quadrilateral with all sides equal must have two pairs of parallel sides to form a parallelogram (and therefore, be a rhombus or a square).
-
Q: What is the difference between a parallelogram and a rhombus?
- A: A parallelogram has two pairs of parallel sides. A rhombus is a special type of parallelogram where all four sides are equal.
-
Q: How can I tell if a quadrilateral is a rhombus?
- A: Show that all four sides are equal, or show that it is a parallelogram with perpendicular diagonals, or show that it is a parallelogram where a diagonal bisects one of the angles.
Conclusion
Quadrilaterals with equal sides, particularly the rhombus and the square, are fundamental shapes with a rich set of properties and wide-ranging applications. Understanding their characteristics and relationships with other geometric figures is essential for building a strong foundation in geometry. By visualizing these properties, mastering the definitions, and practicing problem-solving, you can unlock the power of these seemingly simple shapes.
How do you think these geometric principles are used in fields beyond what we've discussed? Are there any areas where you see the potential for innovative applications of squares and rhombuses in the future?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Electrons Are In Fluorine
Dec 06, 2025
-
How To Calculate Molality From Molarity
Dec 06, 2025
-
Does Plant Cells Have Endoplasmic Reticulum
Dec 06, 2025
-
A Carbohydrate Found In The Cell Wall Of Plants
Dec 06, 2025
-
Linear Inequality In Two Variables Examples
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Sides Of Quadrilateral Are Equal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.